Research
Overall research landscape of our lab is given as follows
Featured
Understanding polarization effects at interfaces
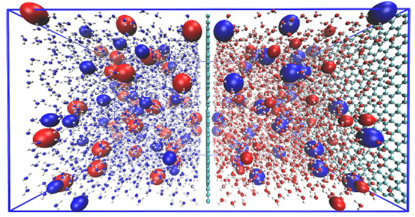
Understanding electrostatic interactions across charged or dielectric interfaces is of critical importance in broad field of science. The interplay of electrostatic interactions through the symmetry-breaking boundaries plays the major role in thermodynamic and dynamic behavior of the system. Recent advances in surface specific spectroscopic techniques have discovered rich structural and chemical properties at interfaces that are distinct from homogeneous systems, although molecular understanding of these complex systems are still challenging. The overall goal of research in my group will be to build a versatile simulation framework for charged interfaces to aid the rational design of functional membrane materials. This includes studies of air/water interface, ion solutions at exotic conditions, polymer electrolytes for next generation batteries, protein interaction with functional bio-membranes and nanoparticles, graphene oxide membranes and its applications.
Designing polymer electrolytes with machine-learning corrected force field
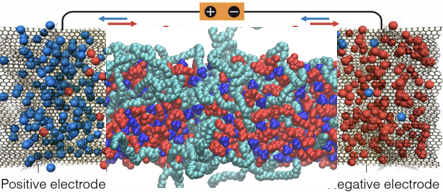
Polymer gel electrolytes are emerging as safe alternative for organic electrolytes in energy storage and wearable devices. Combining polymers with electrolyte solutions or ionic liquids (ILs) enhances the electrochemical stability, mechanical strength and processability while preserving the high conductivity of liquid electrolyte. We’ll systematically study the ion transport and charging mechanisms in polymer gel electrolytes utilizing a machine-learning corrected multi-scale first principles force field.
Graphene oxide (GO) membranes for water purification
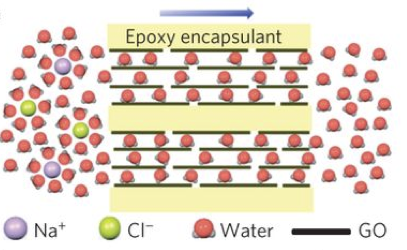
Sub-micrometer sized GO membranes show highly selective water permeation, and applying small electric potential enables precisely controlled water and ion permeation. We focus on understanding previously overlooked polarization effect on the structural and transport properties near the GO surface. Through treatment of both surface and electrolyte polarization effects, we aim to find novel transport mechanisms of confined water and ions, as well as optimizing the separation property of the GO membrane. Image from R.R.Nair et al., Nature Nanotech.(2017)
Role of water in biology
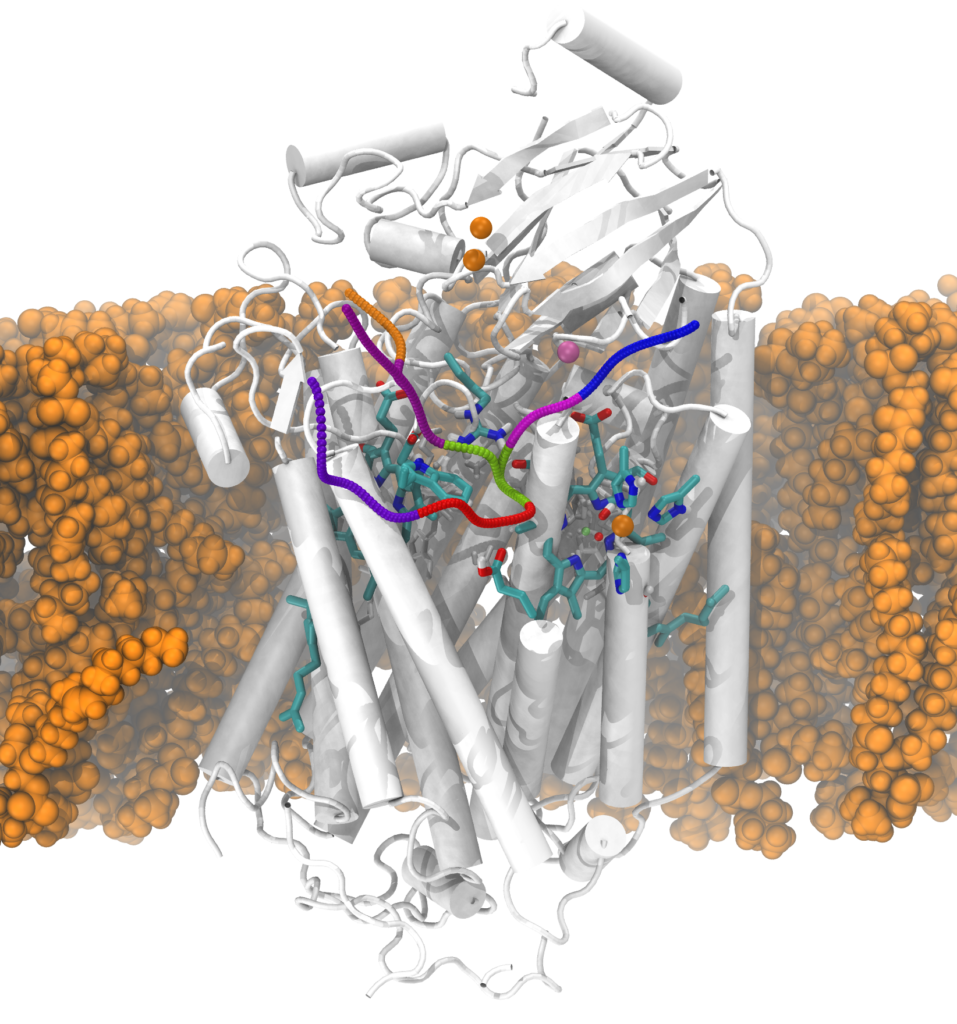
Life has its foundation on water. Not only serving as the solvent media of biology, water plays important role in functional membrane proteins such as in respiration systems, ion channels, ATP synthesis etc. Seeing dynamic pathways of water through complex protein can tell us how the amino acid sequence can communicate with each other, and how they control the reactions that are essential to maintain life. Through multi-scale simulations with the state-of-the-art enhanced sampling techniques we find unique opportunities to answer fundamental questions in life science.
